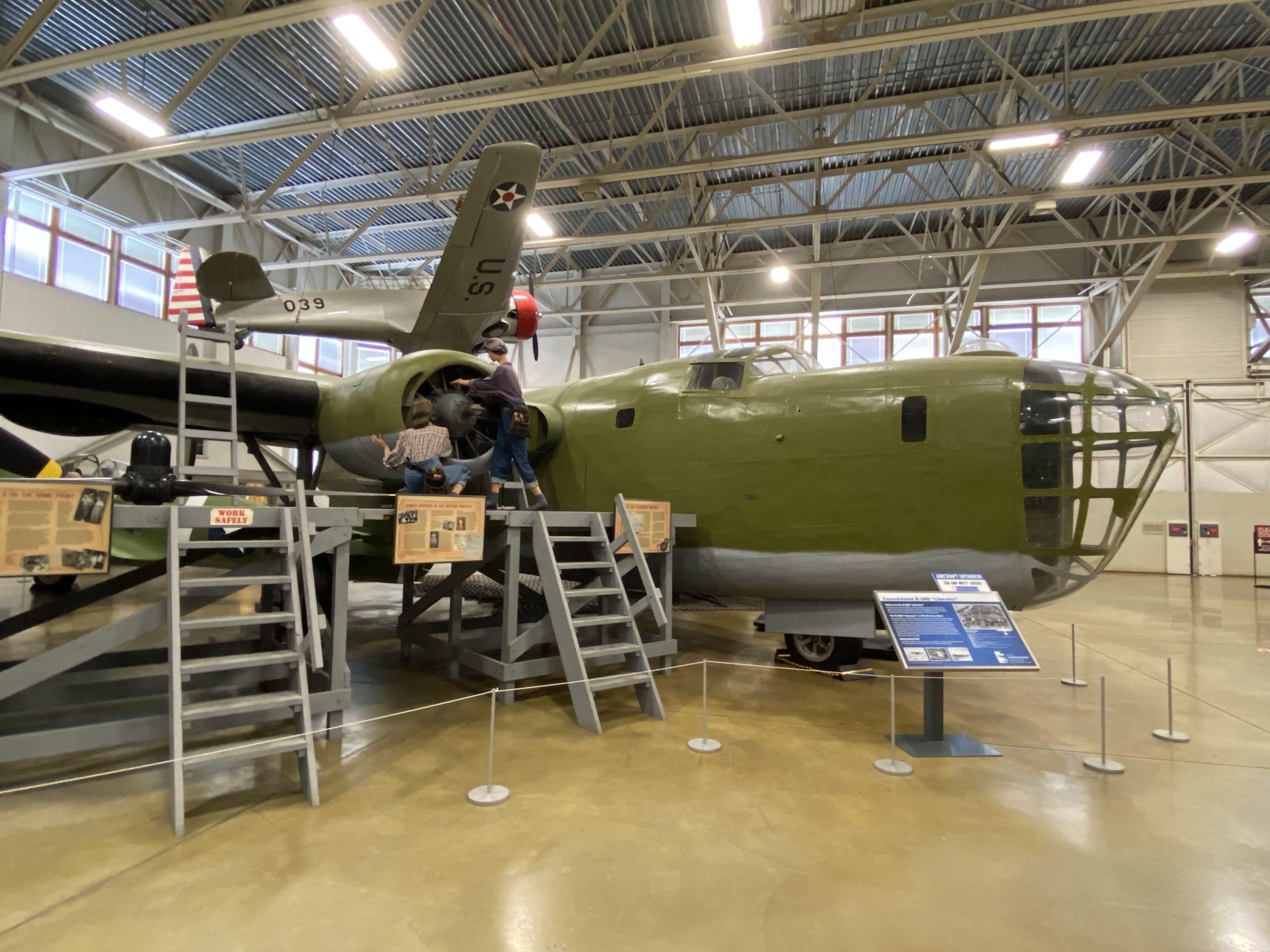
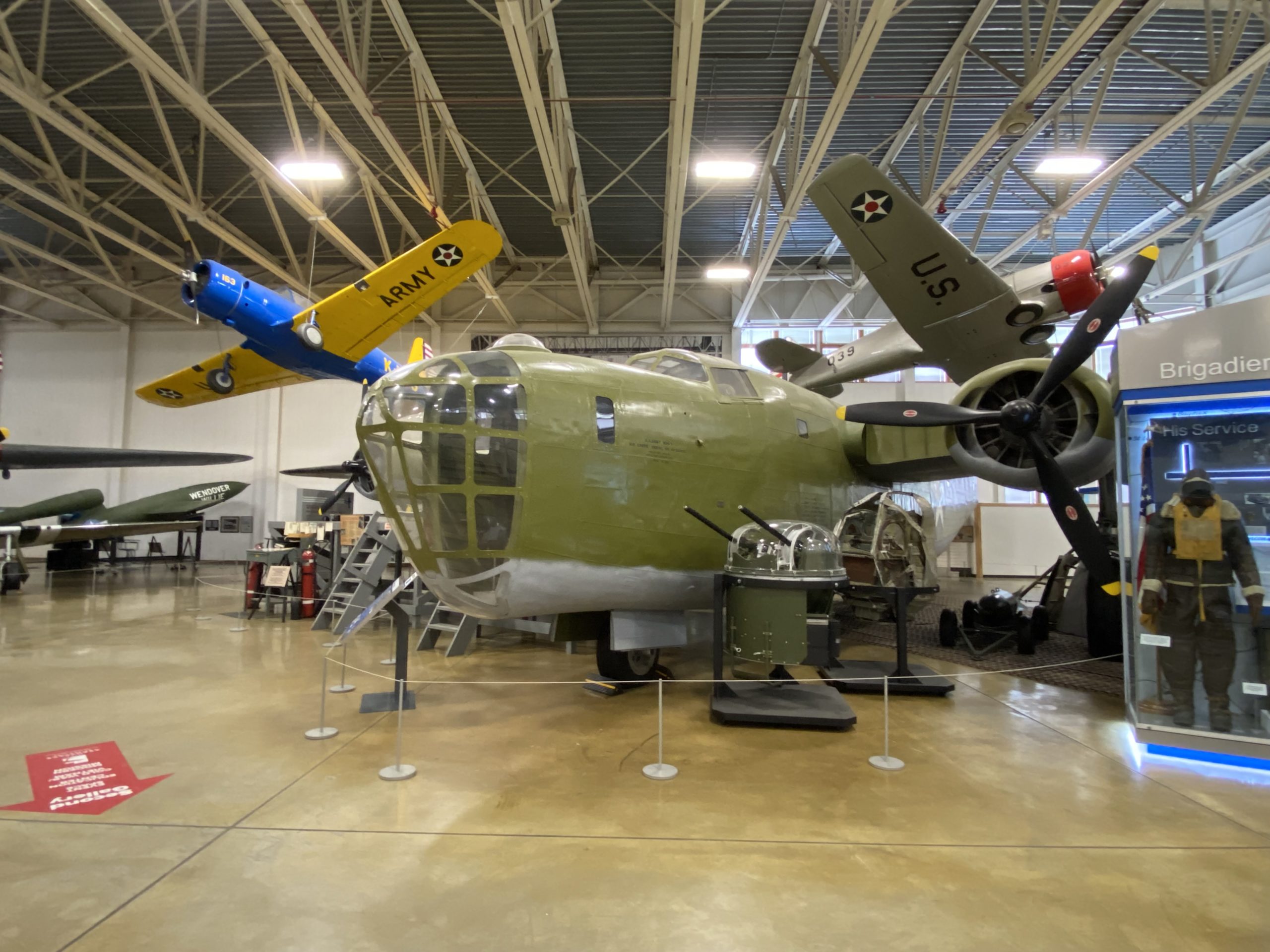
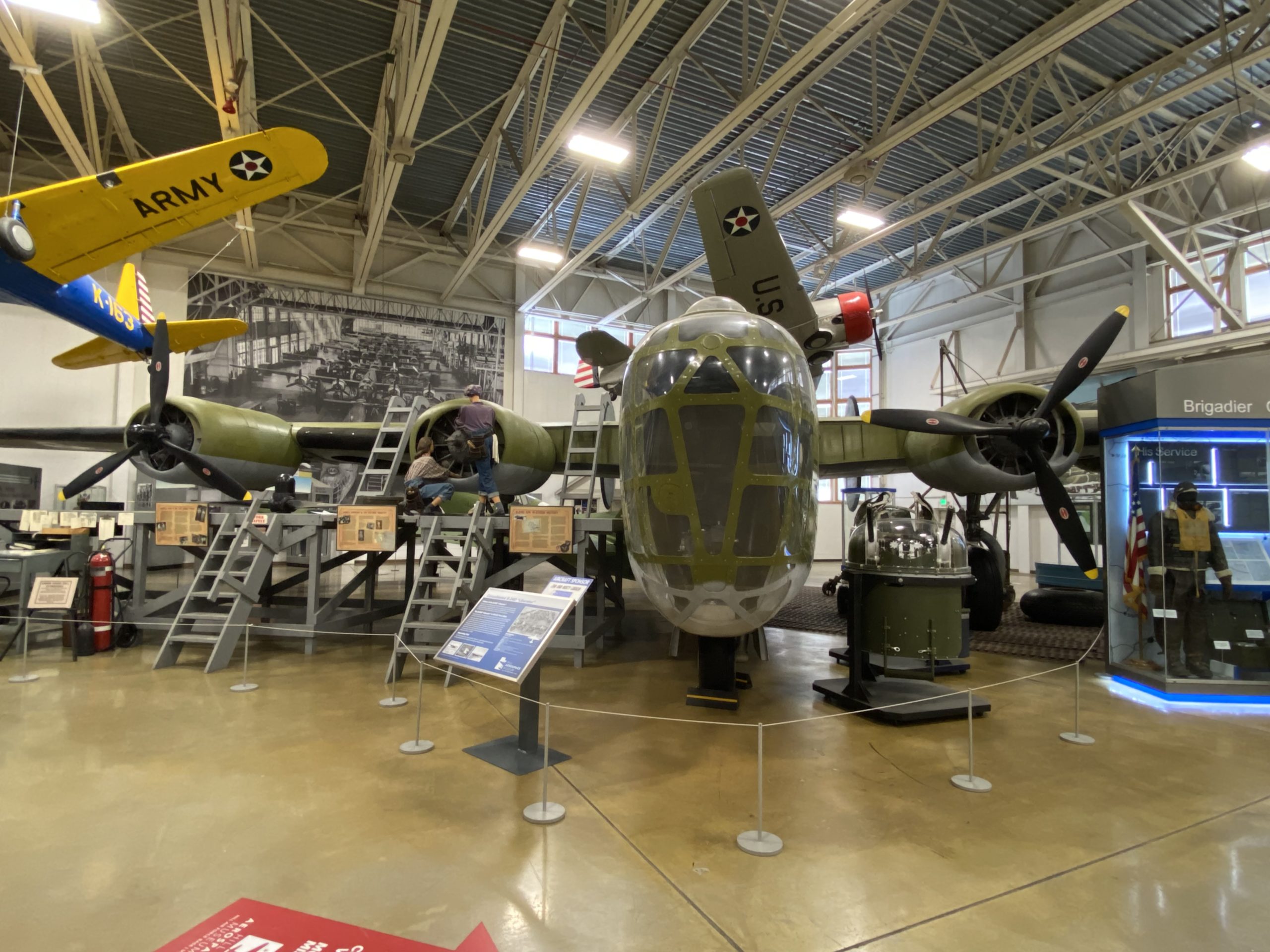
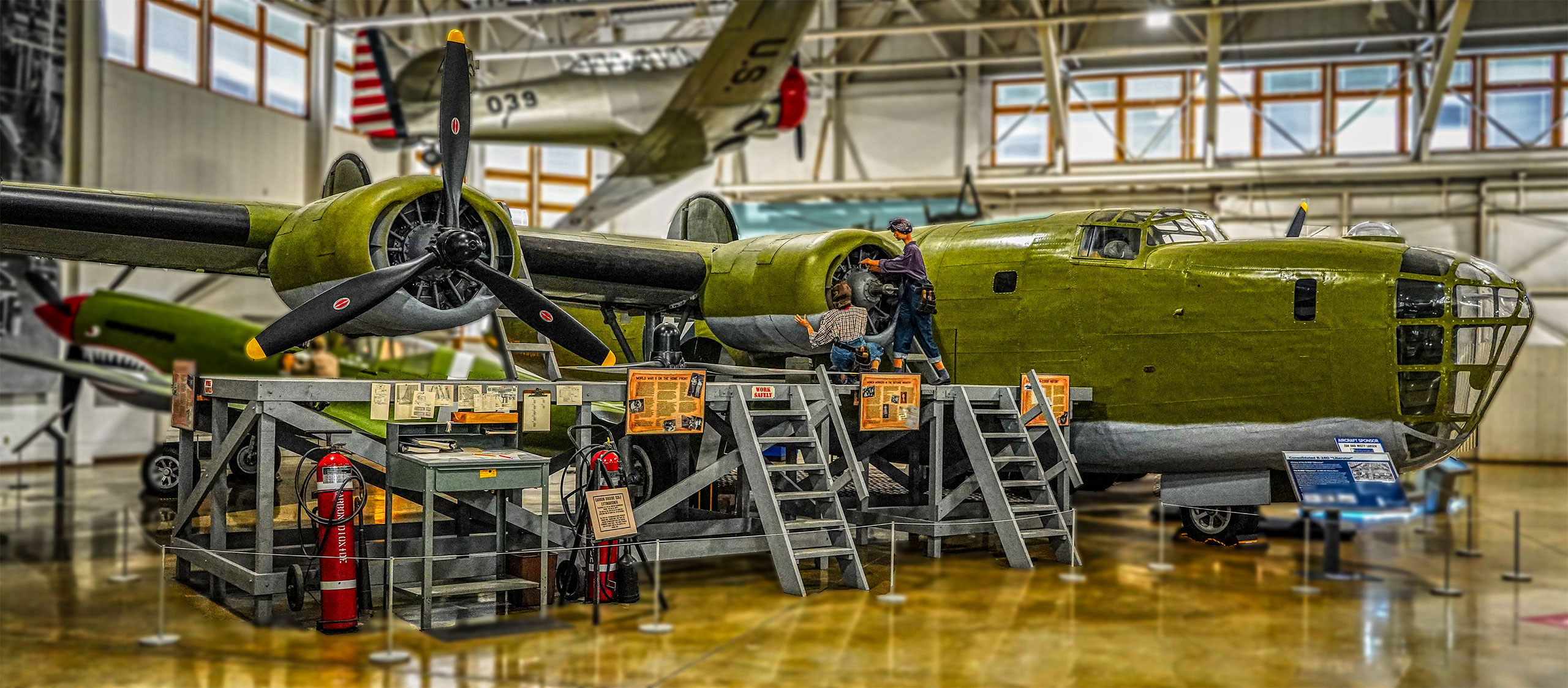
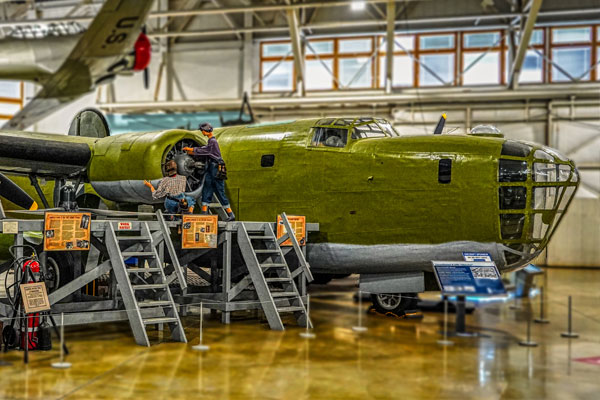
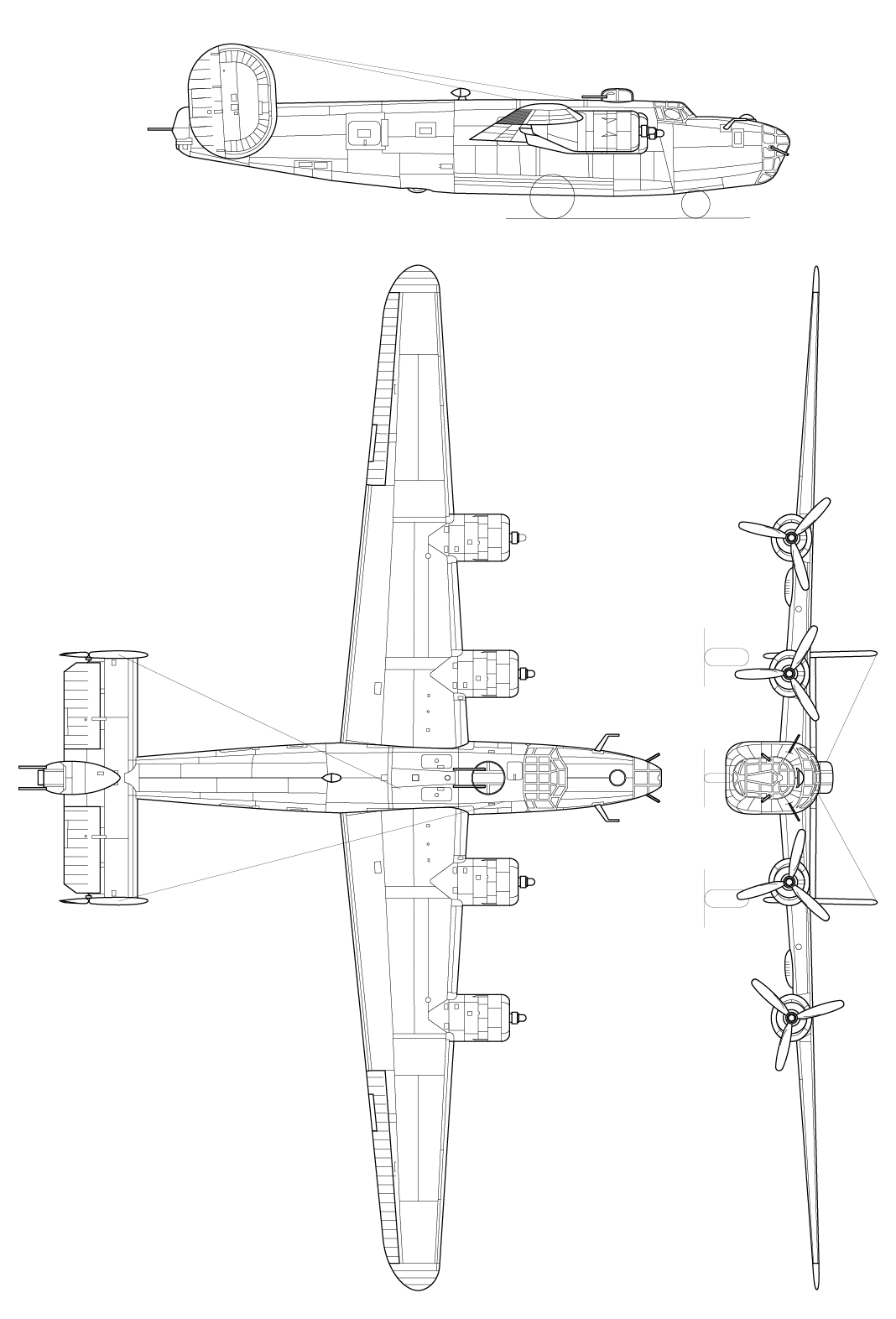
Airmen who flew the Liberator took to naming the airframe the “Flying Coffin” due to its singular entry point near the rear of the aircraft. With only a single point of exit, and far from the majority of the crew, it was nearly impossible for them to leave in an emergency.